-
1 изоляция (кабеля)
изоляция (кабеля)
изоляционные материалы включаемые в кабель с целью обеспечения электрической прочности
[IEV number 461-02-01]EN
insulation (of a cable)
assembly of insulating materials incorporated in a cable with the specific function of withstanding voltage
[IEV number 461-02-01]FR
isolation (d'un câble)
ensemble des matériaux isolants faisant partie d'un câble dont la fonction spécifique est de tenir les conditions de tension
[IEV number 461-02-01]
Тематики
- кабели, провода...
EN
DE
- Isolierung (eines Kabels), f
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > изоляция (кабеля)
-
2 длительный допустимый ток
- courant permanent admissible, m
- courant admissible, m
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > длительный допустимый ток
-
3 экран по изоляции (кабеля)
экран по изоляции (кабеля)
проводящий(ие) слой(и), выполнящий(е) функцию регулирования электрического поля в пределах изоляции. Он (они) может (могут) способствовать получению ровной гладкой поверхности на границах слоя изоляции и устранению пустот на этом участке
[IEV number 461-03-01]EN
screen (of a cable)
conducting layer or assembly of conducting layers having the function of control of the electric field within the insulation
NOTE – It may also provide smooth surfaces at the boundaries of the insulation and assist in the elimination of spaces at these boundaries.
[IEV number 461-03-01]FR
écran (d'un câble)
couche conductrice ou ensemble de couches conductrices ayant pour fonction d'imposer la configuration du champ électrique à l'intérieur de l'isolation
NOTE – Ces couches peuvent aussi permettre de réaliser des surfaces lisses à la limite de l'isolation et contribuer à éliminer les vides à cet endroit.
[IEV number 461-03-01]Тематики
- кабели, провода...
EN
DE
- Leitschicht (eines Kabels), f
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > экран по изоляции (кабеля)
-
4 изолированный провод
изолированный провод
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]EN
core insulated conductor
assembly comprising a conductor and its own insulation (and screens, if any)
[IEC 61892-4, ed. 1.0 (2007-06)]
core-insulated conductor (North America)
assembly comprising a conductor and its own insulation (and screens, if any)
NOTE In North American usage, the core of a cable has been defined as the assembly of components of a cable lying under a common covering such as the sheath (jacket).
[IEC 60092-350, ed. 3.0 (2008-02)]FR
conducteur (isolé)
ensemble comprenant l'âme, son enveloppe isolante et ses écrans éventuels
Note – En Amérique du Nord le terme “core of a cable” a été défini comme l'ensemble des constituants d'un câble disposés sous un revêtement commun, tel que la gaine. L'utilisation de ce terme est déconseillée dans ce sens.
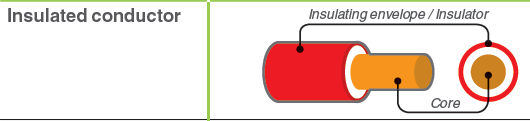
[ IEV ref 461-04-04]Рис. Schneider Electric
Параллельные тексты EN-RU
An insulated conductor is made up of a conductor core and its
insulating envelope.
[Schneider Electric]Изолированный провод состоит из токопроводящей жилы и изоляции провода.
[Перевод Интент]Тематики
- кабели, провода...
EN
- core insulated conductor
- core-insulated conductor
- covered conductor
- covered wire
- insulated conductor
DE
- Ader, f
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > изолированный провод
-
5 кабельный трансформатор тока
кабельный трансформатор тока
-EN
cable type current transformer
a current transformer without primary conductor and primary insulation of its own, which can be mounted over an insulated cable
[IEV number 321-02-04]FR
transformateur de courant pour câble
transformateur de courant sans enroulement primaire et sans isolation propre qui peut être monté sur un câble isolé
[IEV number 321-02-04]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > кабельный трансформатор тока
-
6 разделитель
разделитель
Тонкий слой, выполняющий роль барьера, предупреждающего взаимное вредное воздействие различных компонентов кабеля друг на друга таких, как токопроводящая жила и изоляция или изоляция и оболочка.
[IEV number 461-05-01]EN
separator
thin layer used as a barrier to prevent mutually detrimental effects between different components of a cable, such as between the conductor and insulation or between insulation and sheath
[IEV number 461-05-01]FR
séparateur
couche mince utilisée comme barrière pour éviter les interactions nocives entre deux constituants d'un câble, par exemple entre âme et enveloppe isolante ou entre enveloppe et gaine
[IEV number 461-05-01]Тематики
- кабели, провода...
EN
DE
- Trennschicht (eines Kabels), f
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > разделитель
-
7 изолированная жила (термин употребляется в Северной Америке)
изолированная жила (термин употребляется в Северной Америке)
совокупность элементов, состоящая из жилы, ее изоляции (и экранов, если они есть)
Примечание. В Северной Америке термин «core of a cable» определяется как совокупность компонентов кабеля, расположенных под общим защитным покровом, таким как оболочка. Такое применение этого термина не допустимо
[IEV number 461-04-04]EN
core
insulated conductor
assembly comprising a conductor with its own insulation (and screens if any)
NOTE – In North American usage, the core of a cable has been defined as the assembly of components of a cable lying under a common covering such as the sheath. Such usage is deprecated.
[IEV number 461-04-04]FR
conducteur (isolé)
ensemble comprenant l'âme, son enveloppe isolante et ses écrans éventuels
NOTE – En Amérique du Nord le terme “core of a cable” a été défini comme l'ensemble des constituants d'un câble disposés sous un revêtement commun, tel que la gaine. L'utilisation de ce terme est déconseillée dans ce sens.
[IEV number 461-04-04]Тематики
- кабели, провода...
EN
DE
- Ader, f
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > изолированная жила (термин употребляется в Северной Америке)
-
8 защитный покров
защитный покров
неметаллическое покрытие, накладываемое поверх металлической, как правило, оболочки, обеспечивающее внешнюю защиту кабеля
ПРИМЕЧАНИЕ 1. В Северной Америке термин sheath обычно используется для металлических покрытий, а термин jacket используется только для неметаллических покрытий.
ПРИМЕЧАНИЕ 2. В случае выполнения специального уравнивания потенциалов наружный покров может обеспечивать электрическую изоляцию металлического покрытия, расположенного ниже.
[IEV number 461-05-04]
защитный покров кабеля
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]
защитный покров кабеля
-
[Интент]EN
oversheath
outer sheath
protective (overall) jacket (North America)
non metallic sheath applied over a covering, generally metallic, ensuring the protection of the cable from the outside
NOTE 1 – In North America, the term sheath is generally used for metallic coverings, whereas the term jacket is used only for non-metallic coverings.
NOTE 2 – In case of special bonding, the oversheath may provide electrical insulation of the underlying conducting covering.
[IEV number 461-05-04]FR
gaine externe
gaine extérieure
gaine non métallique appliquée sur un revêtement généralement métallique et assurant la protection externe du câble
NOTE 1 – En Amérique du Nord, le terme “sheath” est utilisé généralement pour les revêtements métalliques tandis que le terme “jacket” est utilisé uniquement pour des revêtements non métalliques.
NOTE 2 – Quand elle est appliquée sur un revêtement conducteur, la gaine externe peut constituer une isolation électrique appropriée dans le cas de connexion spéciale.
[IEV number 461-05-04]Тематики
- кабели, провода...
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Außenmantel, m
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > защитный покров
-
9 разделка конца кабеля
разделка конца кабеля
Последовательное удаление герметической оболочки, защитных и изоляционных слоев на концевом участке кабеля до обнажения токопроводящих жил
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]Тематики
- кабели, провода...
- строительные и монтажные работы
EN
- cable termination (for splicing, insulation etc.)
DE
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > разделка конца кабеля
-
10 прибор класса I
прибор класса I
Прибор, в котором защита от поражения электрическим током обеспечивается не только основной изоляцией, но включает в себя и дополнительные меры безопасности, при которых проводящие доступные части соединены с защитным заземляющим проводом в стационарной проводке установки таким образом, что проводящие доступные части не могут оказаться под напряжением в случае повреждения основной изоляции.
Примечание. Эта мера предосторожности включает в себя защитный провод в шнуре питания.
[ ГОСТ Р 52161. 1-2004 ( МЭК 60335-1: 2001)]EN
class I appliance
appliance in which protection against electric shock does not rely on basic insulation only but which includes an additional safety precaution, in that conductive accessible parts are connected to the protective earthing conductor in the fixed wiring of the installation in such a way that conductive accessible parts cannot become live in the event of a failure of the basic insulation
NOTE - This provision includes a protective earthing conductor in the supply cord.
[IEC 60335-1, ed. 4.0 (2001-05)]FR
appareil de la classe I
appareil dans lequel la protection contre les chocs électriques ne repose pas uniquement sur l'isolation principale mais dans lequel une mesure de sécurité supplémentaire a été prise sous la forme de moyens de raccordement des parties conductrices accessibles à un conducteur de protection faisant partie des canalisations fixes de l'installation de sorte que les parties conductrices accessibles ne puissent devenir dangereuses en cas de défaut de l'isolation principale
NOTE - Ces moyens comprennent un conducteur de protection dans le câble d'alimentation
[IEC 60335-1, ed. 4.0 (2001-05)]Тематики
EN
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > прибор класса I
-
11 шинопровод
система сборных шин
шинопровод
Устройство, представляющее собой систему проводников, состоящее из шин, установленных на опорах из изоляционного материала или в каналах, коробах или подобных оболочках, и прошедшее типовые испытания.
Устройство может состоять из следующих элементов:
- прямые секции с узлами ответвления или без них;
- секции для изменения положения фаз, разветвления, поворота, а также вводные и переходные;
- секции ответвленные.
Примечание — Термин «шинопровод» не определяет геометрическую форму, габариты и размеры проводников.
(МЭС 441-12-07, с изменением)
[ ГОСТ Р 51321. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60439-1-92)]
шинопровод
Жесткий токопровод до 1 кВ заводского изготовления, поставляемый комплектными секциями.
[ПУЭ]
шинопровод
Жесткий токопровод напряжением до 1000 В заводского изготовления, поставляемый комплектными секциями.
[ОСТ 36-115-85]
шинопровод
Жесткий токопровод напряжением до 1 кВ, предназначенный для передачи и распределения электроэнергии, состоящий из неизолированных или изолированных проводников (шин) и относящихся к ним изоляторов, защитных оболочек, ответвительных устройств, поддерживающих и опорных конструкций.
[ ГОСТ Р 53310-2012]EN
busway
A prefabricated assembly of standard lengths of busbars rigidly supported by solid insulation and enclosed in a sheet-metal housing.
[ http://www.answers.com/topic/busway]
busway
Busway is defined by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) as a prefabricated electrical distribution system consisting of bus bars in a protective enclosure, including straight lengths, fittings, devices, and accessories. Busway includes bus bars, an insulating and/or support material, and a housing.
[ http://electrical-engineering-portal.com/siemens-busway-purpose-and-definition]1.1. Шинопроводы по назначению подразделяются на:
- распределительные, предназначенные для распределения электрической энергии;
- магистральные, предназначенные для передачи электрической энергии от источника к месту распределения (распределительным пунктам, распределительным шинопроводам) или мощным приемникам электрической энергии.
1.2. По конструктивному исполнению шинопроводы подразделяются на:
- трехфазные;
- трехфазные с нулевым рабочим проводником;
- трехфазные с нулевым рабочим и нулевым защитным проводником.
2. Основные параметры и размеры
2.1. Основные элементы шинопроводов
2.1.1. Основными элементами распределительных шинопроводов являются:а) прямые секции - для прямолинейных участков линии, имеющие места для присоединения одного или двух ответвительных устройств для секций длиной до 2 м включительно, двух, трех, четырех или более - для секций длиной 3 м;
б) прямые прогоночные секции - для прямолинейных участков линий, где присоединение ответвительных устройств не требуется;
в) угловые секции - для поворотов линии на 90° в горизонтальной и вертикальной плоскостях;
г) вводные секции или вводные коробки с коммутационной, защитной и коммутационной аппаратурой или без нее - для подвода питания к шинопроводам кабелем, проводами или шинопроводом;
д) переходные секции или устройства - для соединения двух шинопроводов на различные номинальные токи или шинопроводов разных конструкций;
е) ответвительные устройства (коробки, штепсели) - для разъемного присоединения приемников электрической энергии. Коробки должны выпускаться с разъединителем, с разъединителем и с предохранителями или с автоматическим выключателем;
з) присоединительные фланцы - для сочленения оболочек шинопроводов с оболочками щитов или шкафов;
и) торцовые крышки (заглушки) - для закрытия торцов крайних секций шинопровода;
к) устройства для крепления шинопроводов к элементам строительных конструкций зданий и сооружений;2.1.2. Основными элементами магистральных шинопроводов являются:
а) прямые секции - для прямолинейных участков линий;
б) угловые секции - для поворотов линий на 90° в горизонтальной и вертикальной плоскостях;
в) тройниковые секции - для разветвления в трех направлениях под углом 90° в горизонтальной и вертикальной плоскостях;
г) подгоночные секции - для подгонки линии шинопроводов до необходимой длины;
д) разделительные секции с разъединителем - для секционирования магистральных линий шинопроводов;
е) компенсационные секции - для компенсации температурных изменений длины линии шинопроводов;
ж) переходные секции - для соединения шинопроводов на разные номинальные токи;
з) ответвительные устройства (секции, коробки) - для неразборного, разборного или разъемного присоединения распределительных пунктов, распределительных шинопроводов или приемников электрической энергии. Коробки должны выпускаться с разъединителем, с разъединителем и предохранителями или с автоматическим выключателем; секции могут выпускаться без указанных аппаратов;
и) присоединительные секции - для присоединения шинопроводов к комплектным трансформаторным подстанциям;
к) проходные секции - для прохода через стены и перекрытия;
л) набор деталей и материалов для изолирования мест соединения секций шинопроводов с изолированными шинами;
м) устройства для крепления шинопроводов к элементам строительных конструкций зданий и сооружений;
н) крышки (заглушки) торцовые и угловые для закрытия торцов концевых секций шинопровода и углов.
2.2.3. В зависимости от вида проводников токопроводы подразделяются на гибкие (при использовании проводов) и жесткие (при использовании жестких шин).
Жесткий токопровод до 1 кВ заводского изготовления, поставляемый комплектными секциями, называется шинопроводом.
В зависимости от назначения шинопроводы подразделяются на:- магистральные, предназначенные в основном для присоединения к ним распределительных шинопроводов и силовых распределительных пунктов, щитов и отдельных мощных электроприемников;
- распределительные, предназначенные в основном для присоединения к ним электроприемников;
- троллейные, предназначенные для питания передвижных электроприемников;
- осветительные, предназначенные для питания светильников и электроприемников небольшой мощности.
[ПУЭ, часть 2]
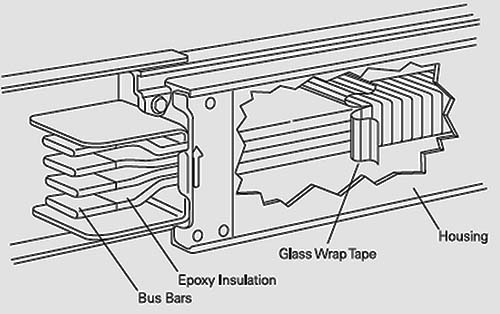
[ http://electrical-engineering-portal.com/siemens-busway-purpose-and-definition]
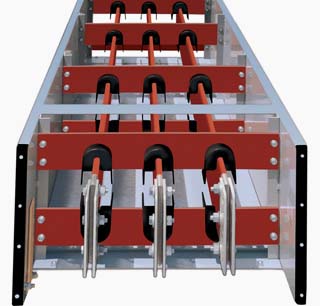
[ http://electrical-engineering-portal.com/standards-and-applications-of-medium-voltage-bus-duct]
Конструкция шинопровода на среднее напряжениеПараллельные тексты EN-RU
A major advantage of busway is the ease in which busway sections are connected together.
Electrical power can be supplied to any area of a building by connecting standard lengths of busway.
It typically takes fewer man-hours to install or change a busway system than cable and conduit assemblies.Основное преимущество шинопровода заключается в легкости соединения его секций.
Соединяя эти стандартные секции можно легко снабдить электроэнергией любую часть здания.
Как правило, установить или изменить систему шинопроводов занимает гораздо меньше времени, чем выполнить аналогичные работы, применяя разводку кабелем в защитных трубах.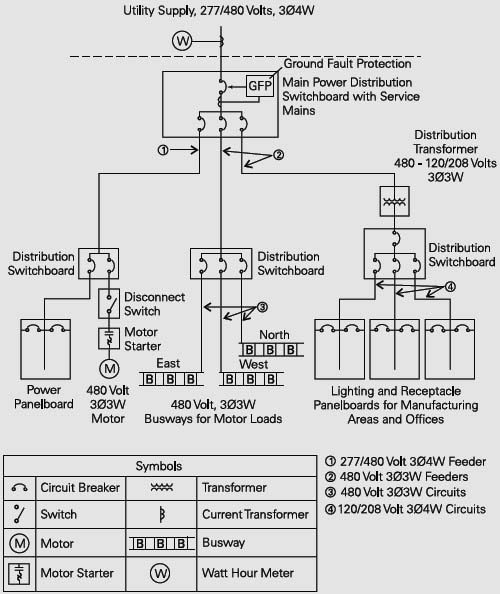
[ http://electrical-engineering-portal.com/siemens-busway-purpose-and-definition]
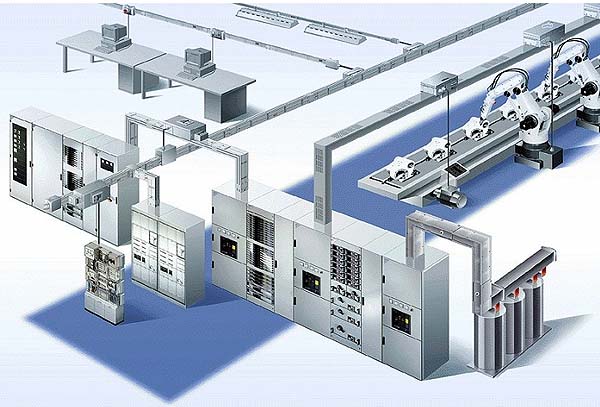
The total distribution system frequently consists of a combination of busway and cable and conduit.
In this example power from the utility company is metered and enters the plant through a distribution switchboard.
The switchboard serves as the main disconnecting means.Как правило, распределение электроэнергии производится как через шинопроводы, так и через проложенные в защитных трубах кабели.
В данном примере поступающая от питающей сети электроэнергия измеряется на вводе в главное распределительный щит (ГРЩ).
ГРЩ является главным коммутационным устройством.
The feeder on the left feeds a distribution switchboard, which in turn feeds a panelboard and a 480 volt, three-phase, three-wire (3Ø3W) motor.
Распределительная цепь, изображенная слева, питает распределительный щит, который в свою очередь питает групповой щиток и электродвигатель.
Электродвигатель получает питание через трехфазную трехпроводную линию напряжением 480 В.The middle feeder feeds another switchboard, which divides the power into three, three-phase, three-wire circuits. Each circuit feeds a busway run to 480 volt motors.
Средняя (на чертеже) распределительная цепь питает другой распределительный щит, от которого электроэнергия распределяется через три трехфазные трехпроводные линии на шинопроводы.
Каждый шинопровод используется для питания электродвигателей напряжением 480 В.The feeder on the right supplies 120/208 volt power, through a step-down transformer, to lighting and receptacle panelboards.
Распределительная цепь, изображенная справа, питает напряжением 120/208 В через понижающий трансформатор щитки для отдельных групп светильников и штепсельных розеток.
Branch circuits from the lighting and receptacle panelboards supply power for lighting and outlets throughout the plant.
[ http://electrical-engineering-portal.com/siemens-busway-purpose-and-definition]Групповые электрические цепи, идущие от групповых щитков, предназначены для питания всех светильников и штепсельных розеток предприятия.
[Перевод Интент]Selection of the busbar trunking system based on voltage drop.
[Legrand]Выбор шинопровода по падению напряжения.
[Перевод Интент]
Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Примечание(1)- Мнение автора карточкиТематики
- изделие электромонтажное
- электропроводка, электромонтаж
Обобщающие термины
Близкие понятия
- электропроводки, выполненные шинопроводами
Действия
- выбор шинопровода по...
- крепление шинопровода к опорным конструкциям
- монтаж шинопроводов
- применение шинопроводов в пожароопасных зонах
- проектирование шинопровода
- прокладка шинопровода
Сопутствующие термины
- вертикальный участок шинопровода
- горизонтальный участок шинопровода
- прямой участок шинопровода
- устройства для крепления шинопроводов
- шинопровод переменного тока на 1600 А
- электрическая сеть, выполняемая шинопроводами
EN
DE
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > шинопровод
-
12 прибор класса 0I
прибор класса 01
Прибор, имеющий по крайней мере повсюду основную изоляцию и включающий зажим для заземления, но снабженный шнуром питания без заземляющего провода и штепсельной вилкой без заземляющего контакта.
[ ГОСТ Р 52161. 1-2004 ( МЭК 60335-1: 2001)]EN
class 0I appliance
appliance having at least basic insulation throughout and incorporating an earthing terminal but having a supply cord without earthing conductor and a plug without earthing contact
[IEC 60335-1, ed. 4.0 (2001-05)]FR
appareil de la classe 0I
appareil ayant au moins une isolation principale dans toutes ses parties et comportant une borne de terre, mais équipé d'un câble d'alimentation ne comportant pas de conducteur de terre, et d'une fiche de prise de courant sans contact de terre
[IEC 60335-1, ed. 4.0 (2001-05)]Тематики
EN
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > прибор класса 0I
См. также в других словарях:
Cable — For other uses, see Cable (disambiguation). 6 inch (15 cm) outside diameter, oil cooled cables, traversing the Grand Coulee Dam throughout. An example of a heavy cable for power transmission … Wikipedia
Insulation-displacement connector — An insulation displacement connector or Insulation piercing connector is a connector that pierces the insulation on a wire to make the connection, removing the need to strip the wire before connecting. Such connections are usually seen in low… … Wikipedia
cable — cablelike, adj. /kay beuhl/, n., v., cabled, cabling. n. 1. a heavy, strong rope. 2. a very strong rope made of strands of metal wire, as used to support cable cars or suspension bridges. 3. a cord of metal wire used to operate or pull a… … Universalium
Cable — /kay beuhl/, n. George Washington, 1844 1925, U.S. novelist and short story writer. * * * (as used in expressions) Cable News Network cable modem cable structure cable television coaxial cable * * * ▪ electronics … Universalium
Cable tester — A cable tester is an electronic device used to verify the electrical connections in a cable or other wired assembly. Generally a cable tester consists of: # A source of electric current, # A volt meter, # A switching matrix used to connect the… … Wikipedia
cable — Noun: A heavy rope, often made of wire; an underground or underseas bundle of wires in insulation used for the transmission of messages by telegraph or telephone. Verb: To send a message by underseas cable … Ballentine's law dictionary
cable paper — noun : a strong paper used as insulation around electric cables … Useful english dictionary
Power cable — This article is about electric power conductors. For portable equipment, see power cord. A power cable is an assembly of two or more electrical conductors, usually held together with an overall sheath. The assembly is used for transmission of… … Wikipedia
Copper wire and cable — Copper has been used in electric wiring since the invention of the electromagnet and the telegraph in the 1820s.[1][2] The invention of the telephone in 1876 proved to be another early boon for copper wire.[3] Today, despite competition from… … Wikipedia
Mineral-insulated copper-clad cable — MIMS redirects here. For multi isotope imaging mass spectrometry, see Isotope mass spectrometry. PVC sheathed MICC cable. Conductor cross section area is 1.5 mm²; overall diameter is 7.2 mm … Wikipedia
Shielded cable — A shielded cable is an electrical cable of one or more insulated conductors enclosed by a common conductive layer. The shield may be composed of braided strands of copper (or other metal), a non braided spiral winding of copper tape, or a layer… … Wikipedia